More actions
Resource access
Most of the data the users of Catglobe will enter into the system will be stored as resources. Resources are all types of records on which there exists a logical reason for giving access rights. An example of a resource is a “report”. Typically you may want to restrict access to a report because it contains information which should not be freely disbursed. You may also want to make a distinction between those who can read a report and those that can edit the information in a report. For each resource we therefore have different access types – or we may also call it different roles in relation to the resource. The three standard roles which are used in the system are:
Observers – user who can view a resource but not change it in any way.
Managers – users who can edit the resource, but not delete it or give other users access to it.
Administrators– users who can perform any action on the resource, including deleting it and giving other users access to it.
The above types of permissions are given to either users or groups to any given resource. Thus, it is also possible to say that a predefined group, e.g. the Board of Directors, can view the report, instead of having to specify the members of the group each time. If the Board of Directors changes it will therefore only be necessary to change the group members, and not necessarily all the resources throughout the system where the Directors should be given access.
Something which often confuses people is the fact that Users and Groups are also resources. Thus, a user can be in the system without having access to himself (i.e. his own resource). This makes a lot of sense if you look at it from a normal business perspective – even though a user knows his own name and salary, we might not want to let him change that information himself!
Another thing that is important to keep in mind is the fact that you can only grant access to resources to which you yourself have administrator rights. If an administrator therefore really wants to have other people help administer the system, he needs to grant other people access to the resources which he initially adds to the database.
It is generally a good idea to allow a few key users to be member of a System Group, which is a group who will have access to any resource in the system. This way you will avoid having resources floating around on the database which nobody can actually access.
Technical Note! The way to create a system group is to first add the group using CatGlobe’s regular user interface, and afterwards add this group’s id to the appropriate web config setting.
Access Inheritance
For all levels of the resource tree it is possible to set the inherit access option. When activating this option a resource will allow users to have the same access rights as they have to the parent of the resource.
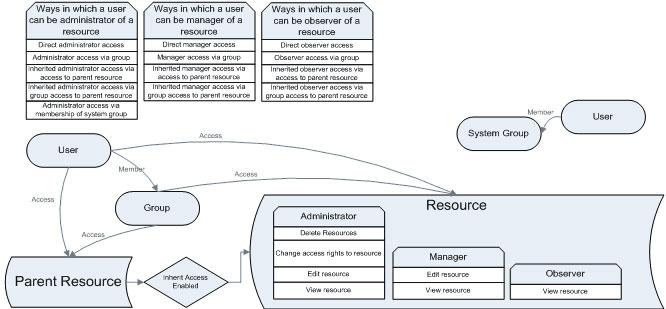
In the same way, when a user is member of a group he will inherit the group’s access rights. If a group has access to a certain screen or record in the system, so will it’s users. A user will only inherit access rights from a group if he himself does not already have better access rights than the group. If he is member of more than one group with access to a specific record he will inherit the access right from the group with the best access rights. Another way of saying it would be that a user’s access to any resource is the cumulative access he has through his own resource or through any group he is member of.
In the above diagram, you can see that a user may have access to a resource through many means.
- He can have access to a resource directly
- He can have access to a resource through being member of a group that has access
- He can have access to a resource through having access to the parent of that resource, where inherit access is enabled between the resources
- He can have access to a resource through being member of a group that has access to the parent resource, where inherit access is enabled between the resources
- He can have access to a resource through being member of the system group
Pages in category "Resource access"
The following 2 pages are in this category, out of 2 total.